Abstract
Introduction: A baseline involved to uninvolved free light chain ratio (FLCr) ≥100 with involved free light chain (iFLC) ≥10 mg/dL is considered a multiple myeloma (MM)-defining event (MDE). However, prior reports have demonstrated that the presence of multimeric light chain aggregates can contribute to falsely increased FLC levels due to impaired renal light chain clearance. Therefore, we aimed to compare the disease progression risk in patients with high versus low urine monoclonal protein (uMCP) excretion in the setting of an elevated serum FLCr.
Methods: We retrospectively evaluated untreated smoldering MM (SMM) and asymptomatic MM patients diagnosed between January 1, 2000 and January 10, 2020. Included patients had a baseline bone marrow plasma cell (BMPC) burden of 10-59% without concomitant end organ damage (hypercalcemia, anemia, renal failure, or lytic lesions on x-ray or cross-sectional imaging; "CRAB" MDE). Patients with a baseline FLCr ≥100 and iFLC >10 mg/dL were included if they had a 24-hour urine collection and electrophoresis. Survival analyses were performed using the Kaplan-Meier method. Progression was defined as treatment for systemic AL amyloidosis or symptomatic MM (typical "CRAB" MDE). SMM patients treated due to evolving biomarkers or "SLiM" MDE (lytic lesions on MRI, BMPC ≥60%, or FLCr ≥100) were censored. Cox proportional hazards models were used for uni- and multivariable analyses. A two-sided p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
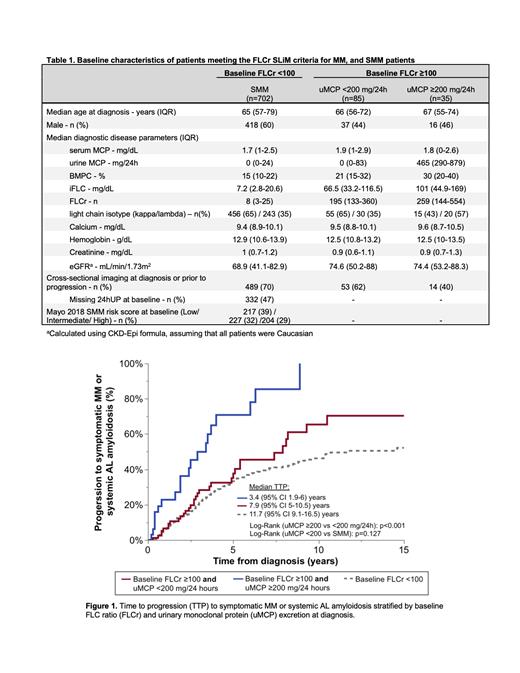
Results: We included 822 patients without MDE besides elevated FLCr (n=120 with FLCr ≥100, n=702 with FLC <100). Patients with a FLC ≥100 were grouped based on 24-hour uMCP excretion (≥200 mg/24h [n=35], <200 mg/24h [n=85]). Among included patients with a baseline FLCr ≥100, the median iFLC was 79.9 (IQR 42.9-131.5) mg/dL and median FLCr was 207.1 (IQR 137.7-400.3). Patients with a FLCr ≥100 and high (≥200 mg/24h) versus low (<200 mg/24h) uMCP excretion had a median iFLC of 101 versus 66.5 mg/dL (p=0.001), median estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) 74.4 versus 74.6 mL/min/1.73m 2 (p=0.505), and median BMPC burden of 30% versus 21% (p=0.088), as shown in Table 1.
The 2-year risk of progression to symptomatic MM or AL amyloidosis was significantly higher in patients with uMCP excretion ≥200 versus <200 mg/24h (36.2% versus 13.5%, respectively; HR 2.79, 95% CI 1.57-4.96, p<0.001, see Figure 1). However, the progression risk was similar in patients with a baseline FLCr <100 versus those with a FLCr≥100 and uMCP <200 mg/24h (log rank p=0.127). After adjusting for baseline eGFR, BMPC burden, iFLC, and light chain isotype, the progression risk was still 2.7 times higher in patients with high versus low uMCP excretion (HR 2.66, 95% CI 1.39-5.10, p=0.003). In patients with a baseline FLCr ≥100 that had cross-sectional imaging at diagnosis or prior to progression confirming the absence of osteolytic lesions, the risk of progression remained significantly higher in patients with a high versus low uMCP excretion (n=14 versus n=53, respectively; HR 4.20, 95% CI 1.86-9.49, p<0.001).
In patients with FLCr ≥100, there were a total of 52 patients with end organ damage at progression (26 [50%] patients with anemia, 8 [15%] with renal failure, 21 [40%] with lytic lesions, 6 [12%] with systemic AL amyloidosis). Among patients who progressed, 5 (25%) of 20 patients with high uMCP excretion and 3 (9.4%) of 32 patients with low uMCP excretion presented with renal failure as the MDE. In patients with baseline high versus low uMCP excretion that experienced renal failure at progression, the median serum creatinine of 2.7 (range 1.9-4.1) versus 2.5 (range 1.9-3.2) mg/dL (p=0.653), median uMCP 4964 (range 738-5910) versus 512 (range 196-734) mg/24h (p=0.052), and median iFLC 388 (range 317-1640) versus 437 (range 199-1030) mg/dL (p=1.00).
Conclusions: Increased uMCP excretion in the setting of a FLCr ≥100 is an unfavourable prognostic marker and is associated with an increased risk of progression. The progression risk in patients with a FLCr ≥100 and low uMCP excretion (<200 mg/24h) is similar to patients with a baseline FLCr <100. Our findings underscore the importance of conducting a 24-hour urine assessment at diagnosis and may help refine the subset of patients with FLCr ≥100 in whom pre-emptive therapy is warranted.
Kapoor: AbbVie: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Research Funding; Glaxo SmithKline: Research Funding; Regeneron Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Ichnos Sciences: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Cellectar: Consultancy; BeiGene: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Sanofi: Consultancy. Gertz: Akcea Therapeutics, Ambry Genetics, Amgen Inc, Celgene Corporation, Janssen Biotech Inc, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Pfizer Inc (to Institution), Sanofi Genzyme: Honoraria; Aurora Biopharma: Other: Stock option; Akcea Therapeutics, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals Inc, Prothena: Consultancy; AbbVie Inc, Celgene Corporation: Other: Data Safetly & Monitoring; Ionis Pharmaceuticals: Other: Advisory Board. Dingli: Novartis: Research Funding; GSK: Consultancy; Alexion: Consultancy; Sanofi: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Apellis: Consultancy. Kumar: Antengene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Bluebird Bio: Consultancy; Roche-Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Astra-Zeneca: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Carsgen: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Oncopeptides: Consultancy; KITE: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Beigene: Consultancy; Tenebio: Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Adaptive: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal